If your website has received a manual penalty from Google, you’ll need to send a reconsideration request to get your website back in the search engine results.
However, you’ll also need to thoroughly address the issues that earned you the penalty in the first place.
Manual penalties are applied when inexperienced or unscrupulous marketers use banned methods to artificially increase the visibility of their websites in the search engines.
Some of the most common among these methods are keyword spam, thin content and aggressive link-building strategies.
It can take an enormous amount of time and effort to reverse the damage, but you’ll need to be able to prove to Google that you have done everything in your power to address the problem before they will reconsider allowing your website back in the search engine results.
1 – Not Enough Effort to Remove Problematic Backlinks
Employing aggressive link-building strategies are among the most common reasons for a website to receive a manual penalty from Google, and if you have ever paid for links before en masse, you’ll have a major problem to deal with.
You will need to be able to convince Google that you have made every reasonable effort to remove links to your website on low-quality directories and irrelevant websites.
However, the problem with reversing this damage is that you only have a limited degree of control over the websites linking to you.
While you should always try to get the problematic links removed, there will be situations where webmasters refuse to cooperate or simply don’t respond at all, in which case you’ll need to use Google Disavow Tool to tell the search engine to ignore the problematic links.
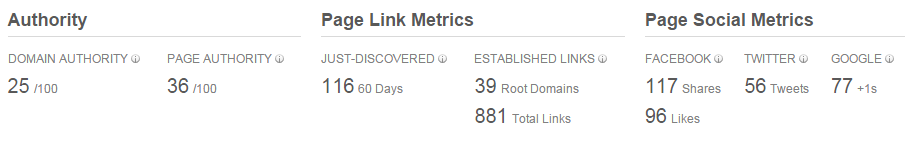 Identify your links with Moz Open Site Explorer
Identify your links with Moz Open Site Explorer
To get started you’ll need to identify your link by conducting a link audit. Then, check out this guide on link removal and Google’s disavow tool.
Related: What makes a good backlink?
2 – Not Providing Enough Explanation
The more honest you are about your website’s history and past SEO-related activities, the better.
You’ll need to admit using any grey- or black-hat SEO tactics so that you can prove to Google that you are making an effort to reverse them.
The more information you can provide, the more likely Google will take your reconsideration request seriously.
Be sure to provide information on your past keyword strategies and link-building activities and show how you have got to the bottom of the problem and made every effort to fix it.
Explain absolutely everything, and don’t leave out any detail not matter how trivial you feel it may be. This can be a long and frustrating part of your reconsideration, but stick with it!
3 – Providing an Incorrectly Formatted Disavow File
Google’s sometimes misunderstood Disavow Tool is invaluable when preparing for a reconsideration request, but it can be quite difficult to use.
You will need to create a special file containing a list of all of the URLs that you want Google to disavow when analysing and ranking your website, and it is wise to include a journal of your manual link removal efforts in the document as well.
You’ll need to make certain that this file is correctly formatted so that the Disavow Tool can make sense of it:
- Save the disavow file in TXT format using UTF-8 or ASCII plain text encoding.
- Disavow entire domains by using the domain: operator, such as domain:badwebsite.com.
- List each individual URL on a new line, including the http:// part.
- When providing a record of your removal efforts, ensure that any comments are preceded by a # on each line.
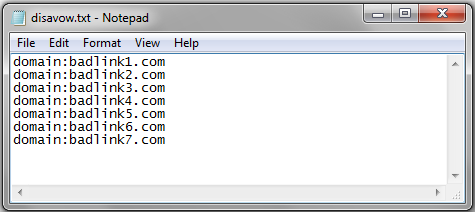
It’s important to remember you cannot upload updates to the list – if you do this, you’ll overwrite your old list. Instead, add to your disavow file and then upload your complete list.
Mighty big problems could occur if you upload a new list and forget to add the old URLs….
4 – Relying too Much on Automation
Although there are some useful tools available to help you collate backlink data, such as Google Webmaster Tools, Majestic SEO, Open Site Explorer and Screaming Frog, you should avoid relying on other companies or tools that claim to specifically find unnatural links.
Ultimately, it is up to you to determine which links are bad and which ones are good, and a third-party tool will be largely ineffective in doing this.
Unfortunately, the only way to properly audit your link profile is to do so manually. You should also avoid relying primarily on Google’s Disavow Tool, since Google makes it quite clear that you should make every effort to remove problematic links before disavowing them.
5 – Not Reworking Thin Content
Websites that have no valuable content to offer, such as those that reuse content from other websites or only publish purely promotional content, are very likely to incur a manual penalty from Google.
If your website has been slammed by Google’s Thin Content Policy, then you’ll need to make every effort to either rewrite it, or better still, start again from scratch.
If you have any URLs with duplicate content, you’ll either need to delete them or list the duplicate pages in robots.txt to tell Google’s robots to disregard them when crawling your website.
Conclusion
Receiving a manual penalty from Google can spell disaster for your website, but armed with a thorough understanding of why the penalty was applied as well as taking every effort to address the problem, your reconsideration quest should go through the system, though it will still take some time for the changes to take effect.
If you are doubtful as to whether you can deal with all of the work involved yourself, you should consider seeking help from an expert who specialises in reversing bad SEO practices.
Your Say!
Have you ever experienced a manual action that lead to a penalty? How did it end up? Did you manage to get your site back in to the SERPS? We’d love to hear your stories. Pop us a comment.
