Page redirects are in constant use on the Internet but are rarely noticed by most Internet users.
These redirect codes inform browsers and search engine robots how to handle a requested URL, and even though they work behind the scenes, they’re a crucial part of search engine optimisation (SEO).
[Tweet “It’s essential to understand the purpose of 301 and 302 redirects when optimising your site.”]
Why Redirects Are Key to SEO
Almost every website needs to use redirects at some point. It may be because content is moved or a site relocates to a new domain. Using the correct redirect keeps web traffic flowing, passes the old pagerank to the new page, and keeps visitor bookmarks working.
Using the wrong type of redirect can seriously damage your SEO strategy.
What Is a 301 (permanent) Redirect?
A 301 redirect tells crawlers that a page has moved permanently to a new URL.
If you move your site to a new domain, or if you’re combining two websites and you want to make sure links to old URLs are redirected to the right pages, you should use a 301.
This tells search engines to pass on any “ink juice” and page authority to the new location. It also prevents people from getting a “404 page not found” error if they use an old link to a page on your site.
How to Use 301 Redirects
You may have a page that can be reached in various ways:
. http://yoursite.com/home
. http://yoursite.com
. http://www.yoursite.com
To prevent Google from thinking these are three separate pages or duplicate content, choose one URL as your preferred (canonical) destination, and use 301 redirects to send web traffic from the other URLs to this one.
This will help prevent the possibility of a Google penalty for republishing duplicate content, which could seriously harm your website in the Google search engine result pages.
301 redirects can also be used for redirecting any 404 error pages, more on this later in the article.
Is There a Limit to How Many 301 Redirects You Can Use?
The most common scenario is when you move from one site to another, and you use 301 redirects from an old page location to a new page location.
There’s no limit to how many 301 redirects you can use on a site; Google will crawl them all. Just remember to only use them when the move is permanent.
What Is a 302 (temporary) Redirect?
The 302 redirect indicates a temporary move. It lets search engines know that any page authority/rank should remain with the old page.
Like a 301 redirect, it will still move your traffic to the new location, but if the new location is permanent, you definitely should not use a 302 redirect. You could risk losing all of your search rankings for those pages.
How to Use 302 Redirects
A good example of when to use a 302 redirect is when your website or page is under construction, and you want people to know it will soon be live. Another use would be for a promotional page that is only going to be temporary.
Using a 302 tells search engines to keep the page rank of the old page and not pass on any link juice. When the original page is ready, you can cancel the redirect and any SEO value should remain.
When to Use Redirects for 404 Error Pages
A 404 page error will occur when a user tries to reach a non-existent page on your website. This happens if they mistype a URL, click an out-of-date or broken link, or if a page has been deleted.
To avoid losing valuable traffic and link juice, always use a 301 redirect to take visitors to another relevant page on their website, or the homepage, rather than displaying a 404 error page.
From a user perspective, a good 404 page can still help people find the information they’re after.
Simply explain to users that the 404 page is showing up because the specific page they searched for is missing.
Then display relevant links or a search box that helps them navigate to other pages on your site.
To find 404 page errors, check your Google Webmaster Tools account to find broken links.
Just go to the Crawl section of your Webmaster Tools account, and look for Crawl Errors.
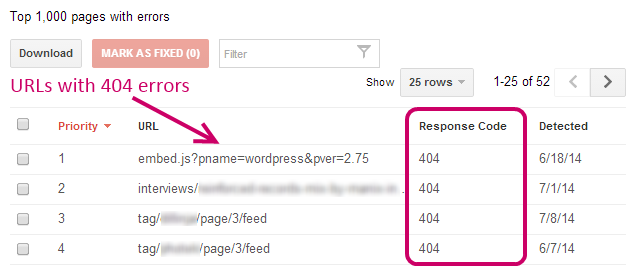
Then use 301 redirects pointing to alternative pages to retain the traffic and link juice.
Similarly, if you have to delete a page but you don’t want to lose the link juice, it’s best to use a 301 to send users and search engines to an alternative page on your site.
Knowing the difference between a 301 and 302 redirect is vital to the success of your long-term SEO strategy.
Implementing Redirects (.htaccess)
To implement either kind of redirect, you’ll first need access to your website’s .htaccess file.
In short, the .htaccess is a configuration file for use on web servers running the Apache Web Server software (the most common server software). It can then be used to alter the configuration of the apache server and enable a myriad of functions and features to support by Apache.
However, .htaccess has one trick that is very useful for SEOs; our much-needed redirects.
Most websites have a .htaccess file already, which can be found in the root directory of your website. If not, you can easily create one using a simple text editor, and naming the resulting file as “.htaccess”.
Please note that in order for this to work your web server needs to have the apache module mod_rewrite installed. If unsure, contact your web hosting provider!
Creating a 301 Redirect
Open your .htaccess and add the following code to implement a 301 redirect.
Redirect 301 /old-page.php http://www.your-domain.co.uk/new-page
This code can be broken down into three sections…
- “Redirect 301” is the command and type of redirect
- “/old-page.php” is the directory path of the page you wish to redirect. Replace this with your own page directory
- And finally, just add the full URL of the new page you wish to add. In the case of our example it was “http:///www.your-domain.co.uk/new-page“
Every time you wish to add a new 301 redirect, just add it on a new line.
Creating a 302 Redirect
This is much the same as above, only you’ll need to specify that this is a 302 redirect within the opening command.
Redirect 302 /old-page.php http://www.your-domain.co.uk/new-page
If you use WordPress, there are plenty of plugins to make this process even easier, such as “Redirection“, or as a feature within popular SEO plugins such as Yoast’s “WordPress SEO“
To set up redirects you’ll need a web hosting service that offers FTP access! Check out our range of excellent website hosting packages and choose the right one for your website. Have a question? Just get in touch with our UK-based support team.
Your Say!
Do you use 301 and 302 directs? Have you searched your website for 404 errors lately? Let us know and ask any questions in the comments below.


2 thoughts on “301 and 302 Redirects: What to Use and When”
Comments are closed.